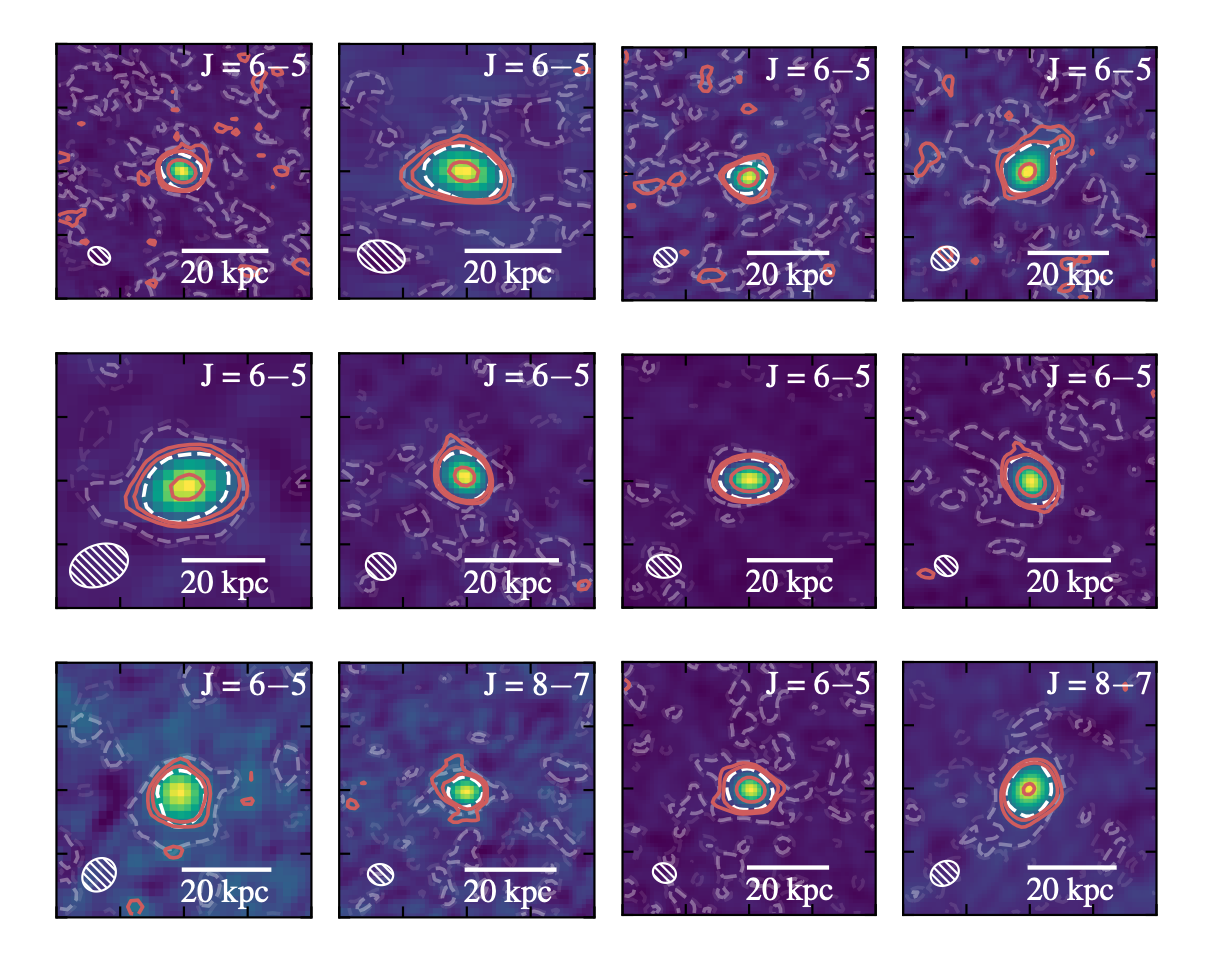
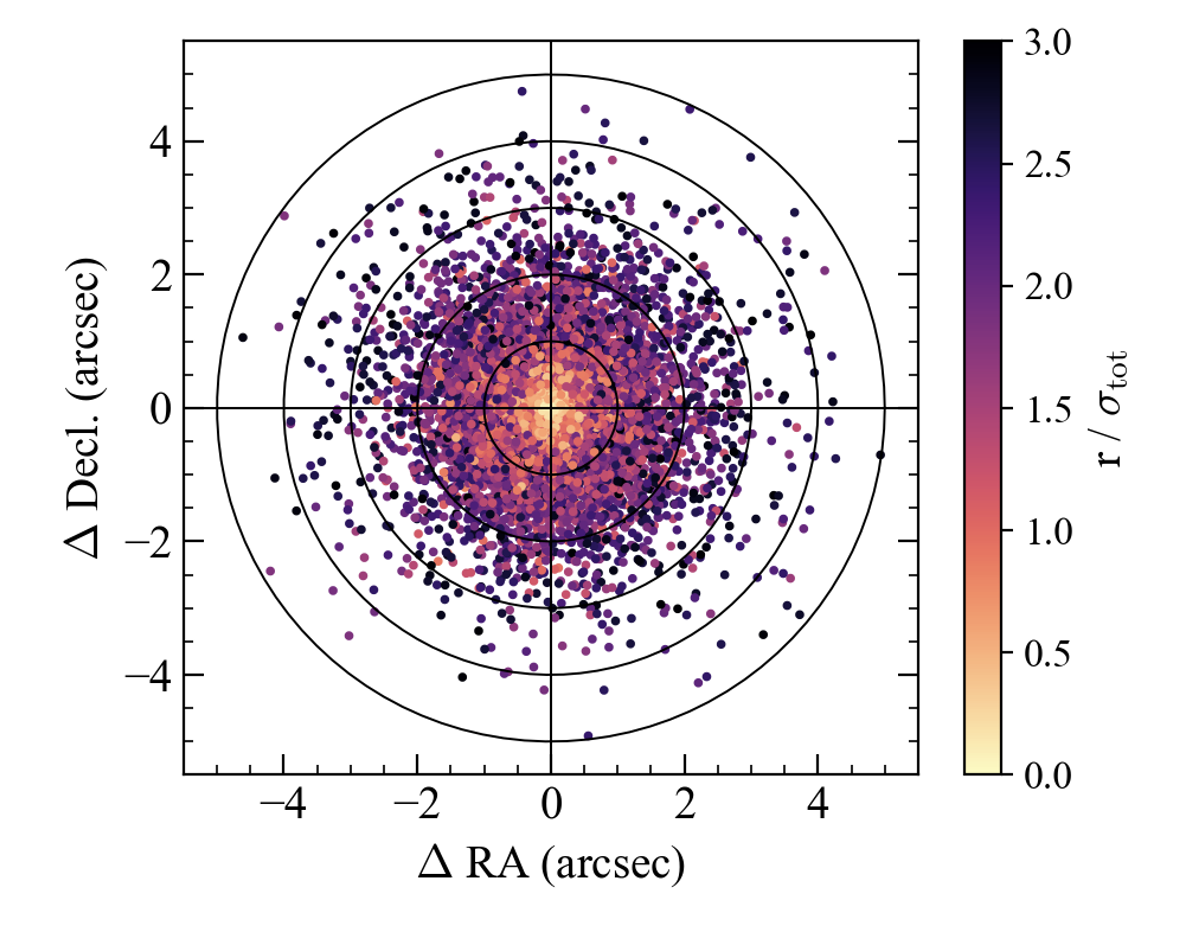
Hi, I'm Dom!
Ph.D. Researcher in Astronomy at Durham University, UK,
applying statistical modeling and quantitative analytics
to molecular and ionised gas dynamics in high-redshift galaxies.
Focused on developing efficient, maintainable code for
large-scale data processing, leveraging Bayesian statistics,
machine learning, and data visualisation to extract
insights from complex datasets.
Find out more about my research below!